Yesterday, I used the Suo Dog image hosting API to create a command line image hosting upload tool. It supports specifying the image hosting service to use and supports uploading single files, multiple files, and multiple directories (non-recursive). Although the code is very simple, I still want to document it (because I want to write an article XD).
Getting the API#
Since we are using an API, we need to get the API first. Let's take a look at the website source code (only the relevant part is excerpted here):
<!--Image hosting selection-->
<div class="bodyer">
<label><input name="keke" checked="checked" type="radio" value="1688">Alibaba Image Hosting</label>
<label><input name="keke" type="radio" value="tieba">Baidu Image Hosting</label>
<label><input name="keke" type="radio" value="360">360 Image Hosting</label>
<label><input name="keke" type="radio" value="taobao">Taobao Image Hosting</label>
<label><input name="keke" type="radio" value="smms">SM.MS Image Hosting</label>
<label><input name="keke" type="radio" value="sohu">Sohu Image Hosting</label>
<label><input name="keke" type="radio" value="jd">JD Image Hosting</label>
</div>
<!--Image upload-->
<script>
var imagesUpload = function (files) {
a = $('input:radio:checked').val();
$(files).each(function (key, value) {
setTimeout(function () {
uurrll = 'https://pic.suo.dog/api/tc.php?type=' + a + '&echo=imgurl'
image_form = new FormData();
image_form.append("file", value);
$.ajax({
url: uurrll,
type: 'POST',
data: image_form,
contentType: false,
cache: false,
processData: false,
async: false,
success: function (data) {
if (typeof (data) == 'string') {
imgurl = data
} else {
imgurl = data.imgurl
}
},
error: function (XMLResponse) {
alert("error:" + XMLResponse.responseText);
}
});
}, 100);
})
};
</script>
The above code is quite clear. It uses a selector to get the value of the currently selected radio button, uses it to concatenate the required API to be requested, and then uses ajax to post the file data to the API. After a successful upload, it returns the URL of the image.
Start Writing#
With the API, the rest is simple. The basic idea is:
- Open the file
- Use
requeststopost - Output the returned image URL
The script uses three packages: requests, click, and os. If any of these packages are missing, you can install them using sudo pip install package_name.
First, set the allowed image file extensions and the API address as global variables:
# Here are several common image formats listed, you can modify them and test other formats yourself
allowedExtension = ['.jpeg', '.bmp', '.jpg', '.png', '.webp']
url = ''
Next, use click to add command line arguments to the main function:
@click.command()
@click.option('--type', '-t', default='1688', type=click.Choice(['1688', 'tieba', '360', 'taobao', 'smms', 'sohu', 'jd']), help='image hosting service.')
@click.argument('paths', nargs=-1, type=click.Path(exists=True, readable=True))
The --type/-t option is used to specify the image hosting service to use, limiting the selection to a certain range of image hosting services. The default is Alibaba Image Hosting. The paths argument accepts multiple path parameters and ensures that the directories exist and are readable.
Then, the main function:
def main(type, paths):
global url
url = 'https://pic.suo.dog/api/tc.php?type={}&echo=imgurl'.format(type)
count = 0
print('\033[33mUploading...\033[0m')
for path in paths:
if os.path.isdir(path):
if not path.endswith('/'):
path += '/'
items = os.listdir(path)
for item in items:
if os.path.isfile(path + item):
count += uploadFile(path + item)
else:
count += uploadFile(path)
print('\033[33mUpload completed, uploaded {} images!\033[0m'.format(count))
The format similar to
\033[33mUploading...\033[0mis used to achieve colored output. For details, see this article.
Using the obtained type, compose the url. Use count to mark the number of uploaded images. Iterate through all the path parameters. If the path parameter is a directory, try to upload all the files in that directory. If the path parameter is a file, try to upload that file directly. Finally, output the number of uploaded images.
Next is the core upload function:
def uploadFile(file):
if os.path.splitext(file)[-1] in allowedExtension:
postContent = {'file': open(file, 'rb')}
with requests.post(url, files=postContent) as response:
print('\033[31m{}\033[0m : \033[4;32m{}\033[0m'.format(
os.path.basename(file), response.text))
return 1
else:
return 0
Check if the extension is allowed. If it is allowed, open the file in binary mode, post it to the API, and output the file name and the uploaded address. Return 1. Otherwise, return 0.
Finally, the usual:
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
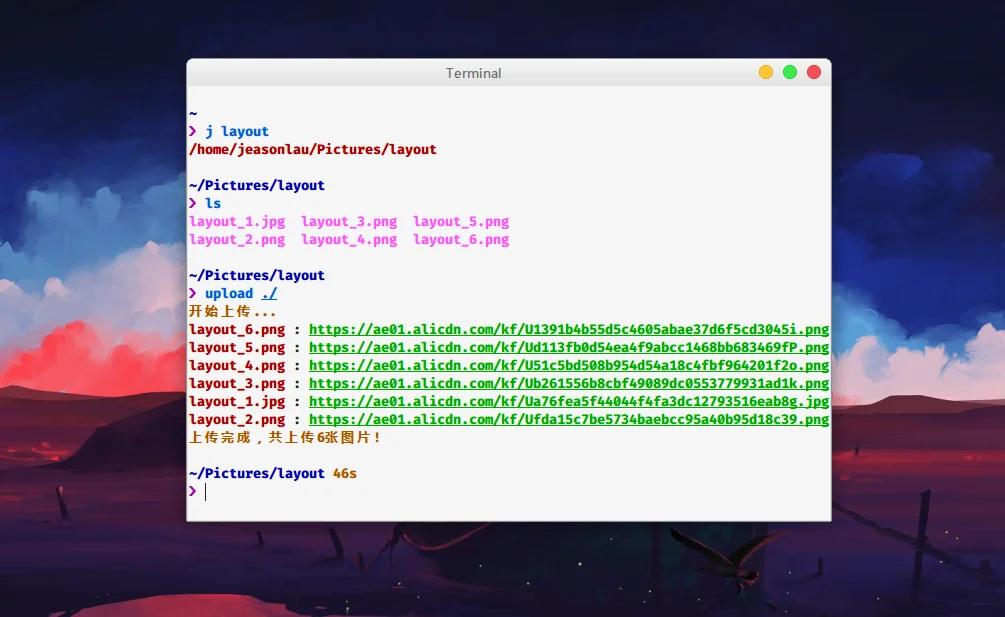
Usage Screenshot#
This screenshot was also uploaded using this tool (using Alibaba Image Hosting /
--type 1688)
Conclusion#
Ah, I didn't expect that such a few lines of code could generate such a long article! (Silly)
Currently, the Alibaba Image Hosting works fine, but the other image hosting services have not been tested. If you have any questions, please let me know.